Motion correction for dMRI images¶
Now that we have a mask highlighting the spinal cord, we can apply motion correction to the volumes of the dMRI data.
The motion correction algorithm¶
SCT features a complex motion correction algorithm inspired by [Xu et al., Neuroimage 2013]. The key aspects of this algorithm are as follows:
SliceReg: Slice-wise registration regularized along the Z direction (based on the function antsSliceRegularizedRegistration from ANTs, and described in [De Leener et al., Neuroimage 2017]).
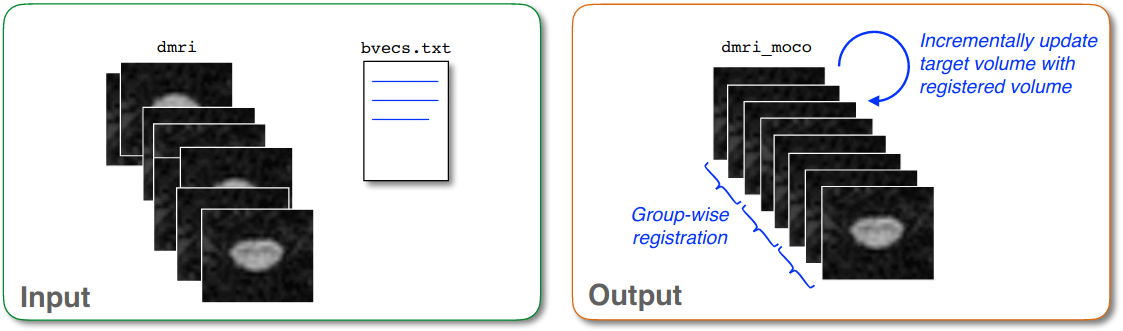
Grouping: The algorithm performs group-wise registration between groups of successive dMRI volumes. If your data has a very low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), you can use the flag
-gto increase the number of successive images that are averaged into a group in order to have sufficient SNR to estimate a reliable transformation.Iterative average: After registering a new group to the target image (which is usually the first DWI group), the target is averaged with the newly registered group in order to increase the SNR of the target image.
Outlier detection: If a detected transformation is too large, it is ignored and the previous transformation is used instead.
Masking: You can use the flag
-mto provide a spinal cord mask, in order to estimate motion of the cord while ignoring the rest of the tissue.
Applying the algorithm¶
To apply the algorithm, we use the sct_dmri_moco command:
sct_dmri_moco -i dmri.nii.gz -m mask_dmri_dwi_mean.nii.gz -bvec bvecs.txt \
-qc ~/qc_singleSubj -qc-seg dmri_dwi_mean_seg.nii.gz
- Input arguments:
-i: The input dMRI image.-m: A mask used to limit the voxels considered by the motion correction algorithm.-bvec: A text file with three lines, each containing a value for each volume in the input image. Together, the the three sets of values represent the(x, y, z)coordinates of the b-vectors, which indicate the direction of the diffusion encoding for each volume of the dMRI image.-qc: Directory for Quality Control reporting. QC reports allow us to evaluate the results slice-by-slice.-qc-seg: Segmentation of spinal cord to improve cropping in QC report.
- Output files/folders:
dmri_moco.nii.gz: The motion-corrected 4D dMRI image.dmri_moco_b0_mean.nii.gz: The time-average of the motion-corrected 3D volumes withb == 0.dmri_moco_dwi_mean.nii.gz: The time-average of the motion-corrected 3D volumes withb != 0. (This image is what will be used for the template registration.)moco_params.tsv: A text file that provides a simplified overview of the motion correction, to be used for quality control. It contains the slicewise average of the axial (X-Y) translations for each 3D volume. (In reality, though, each slice of each volume will have had a different translation applied to it.)moco_params_x.nii.gz: A 4D image with dimensions[1, 1, z, t]. Each voxel contains thextranslation corresponding to eachzslice across eachtvolume.moco_params_y.nii.gz: A 4D image with dimensions[1, 1, z, t]. Each voxel contains theytranslation corresponding to eachzslice across eachtvolume.